Graphic by Robert Wood Johnson Foundation
Adverse childhood experiences
Childhood events can shape health issues later on in life
March 5, 2019
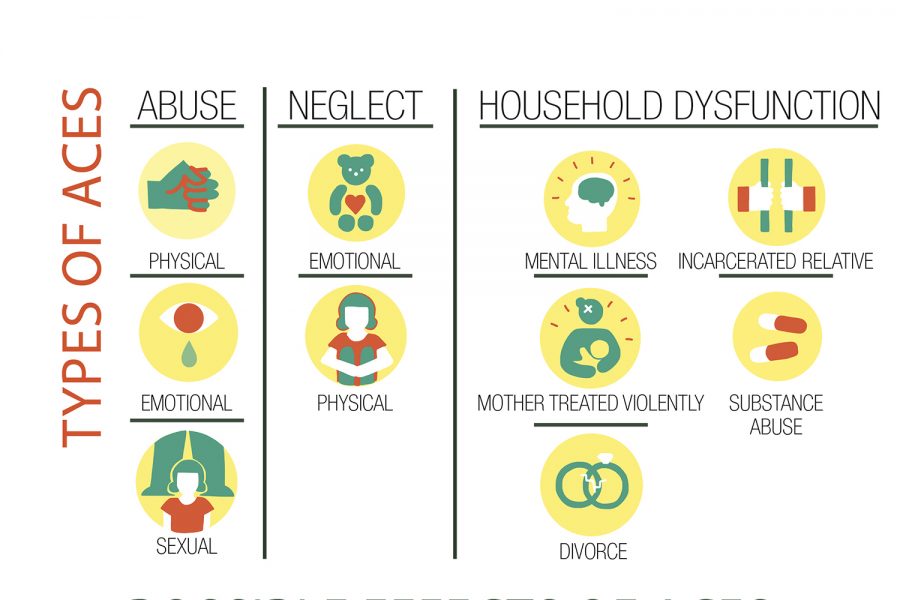
Adverse Childhood Experiences are traumatic or stressful events that occur before the age of 18. ACEs include abuse, neglect or household dysfunction. An ACE could be identified as a multitude of events, such as divorce, domestic violence, emotional neglect or sexual abuse.
ACEs trigger toxic stress, which activates the brain’s fight- or-flight stress release system (FFSR). This is a two-part system. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) triggers the activation, and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) returns the body to its normal state. This response is used to protect people from immediate physical danger, which then results in emotional stress, but more recently, this stress has been triggered by memories of negative experiences. The repetition of the FFSR system causes two types of life-long consequences.
Physical Health Consequences:
Chronic activation of the FFSR system can result in unhealthy eating habits and sleeping patterns, racing heartbeats, back pain and even the shut down of body systems. Consistent shutting down of the digestive system can cause migraines, hair loss, skin rashes and dizziness.
Mental Health Consequences:
Tolls on mental health can appear in the form of depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts, feelings of hopelessness, difficulty concentrating, or the need to be in control.
There are four common coping skills that respond to the FFSR system:
(Fight) Yelling, crying or physically lashing out. This is more common with children who do not understand how to express their emotions, resulting in the need to fight.
(Freeze) Shutting down when facing conflict. This skill is learned in childhood and teenage years. Instead of reacting or engaging, people freeze because it has kept them safe.
(Appease) Consistent concern for others feelings and the need to appease is another coping skill. This is used in attempts to prevent conflict.
(Deflect) Trying to manipulate and blame others for one’s guilt is considered denial, deflecting the effects of the FFSR system.